Common Challenges and Solutions When Using Kotter’s Model: Navigating Organizational Change
Organizational change is an inevitable reality for any business, big or small. With the constantly evolving market trends and consumer demands, companies need to adapt and evolve to stay competitive and relevant. However, managing change within an organization can be a daunting task. It requires a well-planned and structured approach to ensure successful implementation and acceptance by all stakeholders. This is where change management models, like Kotter’s 8-Step Model, come into play. Developed by renowned leadership expert, John Kotter, this model provides a comprehensive framework for navigating organizational change. In this article, we will delve into the common challenges that businesses face when using Kotter’s model and offer solutions to overcome them. So, whether you are a seasoned leader or a new manager, join us as we explore the complexities of change management and how Kotter’s model can help you overcome them.
Organizational change can be a daunting task, but with the right strategies, techniques, and tools, it can be effectively navigated. In this article, we will delve into the common challenges faced when using Kotter’s 8-Step Model for change management, and provide solutions to overcome them.
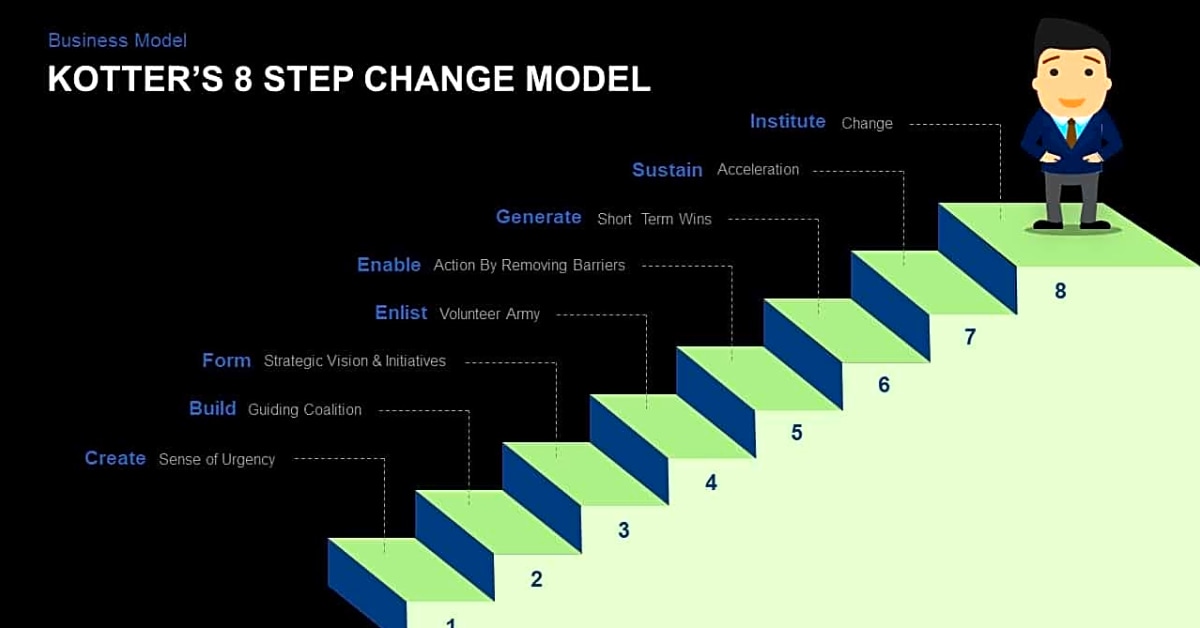
Kotter’s 8-Step Model is a proven framework for successfully implementing change in organizations. It consists of eight steps that guide leaders through the process of initiating and managing change. Let’s take a closer look at each step and how it can be applied in change management.
Step 1: Create a Sense of Urgency
The first step in Kotter’s model is to create a sense of urgency. This involves communicating the need for change and involving all stakeholders in the process. One common challenge during this step is resistance from employees who may be comfortable with the current way of doing things. To overcome this, leaders can use effective communication to explain the reasons for change and involve employees in the decision-making process. For example, a company that successfully created a sense of urgency was Apple when they launched the iPod. They communicated the need for change in the music industry and involved stakeholders such as musicians, record labels, and consumers in the development of the iPod.
Step 2: Form a Powerful Coalition
The next step is to form a powerful coalition of individuals who support the change and have the influence to make it happen. This can be challenging as it requires getting buy-in from key decision-makers and influencers within the organization. To overcome this challenge, leaders can identify and involve key stakeholders early on in the process and provide them with a clear understanding of their roles and responsibilities in driving the change forward.
Step 3: Create a Vision for Change
Having a clear vision for change is crucial in Kotter’s model. This involves defining the desired outcome of the change and communicating it to all stakeholders. A common challenge during this step is a lack of resources, which can hinder the implementation of the change. To address this, leaders can identify potential resource constraints early on and develop a plan to secure the necessary resources. For example, when Netflix first shifted from renting DVDs to streaming content, they faced resistance from major movie studios who did not want to provide them with their content. However, Netflix was able to secure the necessary resources by partnering with smaller studios and investing in original content.
Step 4: Communicate the Vision
Communicating the vision is essential in gaining buy-in and support from employees. It involves using various communication channels to consistently communicate the vision and its benefits. A common challenge during this step is resistance from employees who may not understand or agree with the vision. To overcome this, leaders can use different forms of communication such as town hall meetings, newsletters, and one-on-one discussions to address any concerns and gain employee support.
Step 5: Empower Others to Act on the Vision
In this step, leaders must empower others to take action and make the necessary changes to achieve the vision. This can be challenging as it requires giving up control and trusting others to make decisions. To overcome this, leaders can provide training and support to employees to develop the skills needed for success. For instance, when Google acquired YouTube, they empowered the founders to continue making decisions and growing the platform while providing them with resources and support.
Step 6: Create Short-Term Wins
Creating short-term wins is crucial in keeping employees motivated and showing progress towards the vision. A common challenge during this step is encountering setbacks that can demotivate employees. To address this, leaders can celebrate small wins and use them as motivation to continue towards the larger goal. For example, when Ford implemented their One Ford plan, they celebrated each milestone achieved, such as increasing market share, to keep employees motivated.
Step 7: Consolidate Gains and Produce More Change
Consolidating gains involves building on the short-term wins and leveraging them to make further changes. This can be challenging as it requires balancing the need for continuous improvement with maintaining stability. To overcome this, leaders can involve employees in identifying areas for improvement and implementing changes in a systematic manner. For instance, when Toyota implemented their Toyota Production System, they continuously sought input from employees to identify areas for improvement and implemented changes in a structured manner.
Step 8: Anchor New Approaches in Corporate Culture
The final step in Kotter’s model is to anchor new approaches in the corporate culture. This involves embedding the changes into the organization’s processes and systems to ensure they become a part of the company’s culture. A common challenge during this step is maintaining momentum and avoiding a return to old habits. To address this, leaders can reinforce the changes through training and continuous communication, and recognize and reward employees who embody the new culture.
In conclusion, Kotter’s 8-Step Model provides a comprehensive framework for successfully navigating organizational change. By understanding each step and addressing common challenges with effective solutions, leaders can effectively implement change and achieve their desired outcomes. Real-life examples show the effectiveness of these strategies in various industries, making Kotter’s model a valuable tool for any organization facing the challenges of change management.
Creating a Sense of Urgency
One of the first challenges when implementing Kotter’s 8-Step Model for change management is creating a sense of urgency within the organization. Without a sense of urgency, it can be difficult to get individuals and teams motivated to embrace change and actively participate in the process.
In order to overcome resistance and gain support, it is important to clearly communicate why change is necessary and the potential consequences of not making changes. This can be done through various means such as town hall meetings, emails, and one-on-one conversations with key stakeholders.
It is also important to involve employees in the change process and give them a sense of ownership. This can be done by soliciting their input, addressing their concerns, and actively involving them in decision-making processes.
Additionally, providing incentives and rewards for those who embrace change and actively participate in the process can help create a sense of urgency and motivation.
By effectively communicating the need for change, involving employees in the process, and providing incentives and rewards, organizations can overcome resistance and gain support for Kotter’s 8-Step Model for change management.
Generating Short-Term Wins
In the world of organizational change, celebrating small victories can have a big impact on the success of a project. This is especially true when using Kotter’s 8-Step Model for change management.
Kotter’s model emphasizes the importance of creating short-term wins as a way to build momentum and keep employees engaged and motivated during times of change. These small wins serve as tangible evidence that the change is making progress and can help to alleviate any resistance or skepticism from employees.
By celebrating these short-term wins, leaders can boost morale, increase employee buy-in, and show appreciation for their hard work and dedication. This positive reinforcement can also help to create a culture of success and encourage employees to continue striving towards the larger goal.
It’s important for leaders to recognize and celebrate these small victories, whether it’s through verbal praise, team recognition, or even small rewards. This not only shows appreciation for employees’ efforts, but it also reinforces the importance and impact of their work.
Ultimately, celebrating small victories is crucial for navigating organizational change using Kotter’s 8-Step Model. It helps to keep employees motivated, engaged, and focused on the end goal, while also creating a positive and supportive work environment.
Anchoring New Approaches in the Company’s Culture
One of the key challenges when implementing change using Kotter’s 8-Step Model is embedding the new approaches into the company’s culture. This requires not only changing processes and systems, but also shifting mindsets and behaviors.
In order to successfully anchor new approaches in the company’s culture, leaders must first clearly define the desired culture and values that align with the change. This includes involving employees in the process and creating a shared understanding of why the change is necessary and how it will benefit both the organization and its employees.
Next, leaders must lead by example and demonstrate the desired behaviors themselves. This helps to create a culture of accountability and shows employees that the change is being taken seriously.
Communication is also crucial in embedding change into the organizational culture. Leaders must consistently communicate the why, what, and how of the change to employees at all levels of the organization. This helps to build trust and transparency and keeps everyone aligned and on track.
Finally, it’s important to recognize and reward employees who exemplify the desired behaviors and contribute to embedding the change into the culture. This reinforces the importance of the change and creates a positive feedback loop.
Developing a Vision and Strategy
When implementing change in an organization, having a clear and compelling vision is crucial for success. It helps employees understand the purpose of the change and motivates them to work towards achieving it. However, crafting a vision that resonates with everyone can be a difficult task. Here are some tools that can help in developing a strong and effective vision.
Kotter’s 8-Step Model:
Kotter’s model provides a framework for creating a vision that aligns with the overall goal of the organization. It emphasizes the importance of involving employees at all levels in the development of the vision, as this creates a sense of ownership and commitment towards achieving it.
SWOT Analysis:
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis can help identify the internal and external factors that may impact the success of the vision. This can guide in making necessary adjustments to ensure the vision is achievable and sustainable.
Brainstorming Sessions:
Collaborative brainstorming sessions involving employees from different departments can generate diverse ideas and perspectives, leading to a more comprehensive and inclusive vision. This also fosters teamwork and promotes a sense of unity within the organization.
Storytelling:
Using storytelling techniques can make the vision more relatable and engaging for employees. It helps create an emotional connection with the vision, making it more memorable and inspiring.
Communicating the Change Vision
One of the most crucial aspects of successful change management is effectively communicating the change vision to all stakeholders involved. Without clear and consistent communication, employees may feel confused, resistant, or uncertain about the changes being implemented. This can lead to a lack of buy-in and hinder the success of the change process.
To ensure effective communication during change management, here are some strategies to consider:
- Start with a clear and compelling vision: The first step in communicating change is to have a clear and compelling vision that outlines the reasons for change and the desired outcomes. This will help employees understand the purpose behind the changes and how they fit into the bigger picture.
- Use multiple channels: Different people prefer different communication methods, so it’s important to use a variety of channels to reach all employees. This can include team meetings, emails, newsletters, intranet updates, and more.
- Be transparent: Open and honest communication is key during change management. Be transparent about the changes being made, why they are necessary, and how they will impact employees. This will help build trust and credibility.
- Listen to feedback: Communication is a two-way street. Make sure to actively listen to employees’ concerns, questions, and feedback. This will show that their opinions are valued and can also help address any potential roadblocks.
Consolidating Gains and Producing More Change
After successfully implementing the first six steps of Kotter’s model, the organization should have experienced some initial changes and progress. However, it is important to not become complacent and lose momentum. This is where the seventh step, Consolidating Gains, comes into play.
Consolidating gains involves celebrating and acknowledging the progress made so far, as well as reinforcing the new behaviors and processes that have been put in place. This helps to solidify the changes and make them a part of the organizational culture.
In addition, producing more change is also essential in this step. While the initial changes may have been successful, it is important to continue making improvements and adapting to new challenges. This helps to sustain momentum and avoid relapse into old ways of doing things.
One way to produce more change is by continuously seeking feedback from employees and stakeholders. This allows for ongoing improvement and ensures that the changes are aligned with the organization’s goals.
Another important aspect of this step is to recognize and reward employees who have contributed to the success of the change implementation. This not only motivates them to continue supporting the changes, but also encourages others to do the same.
Overall, consolidating gains and producing more change is crucial for sustaining organizational transformation and avoiding relapse into old habits. By continuously improving and reinforcing the changes, the organization can successfully navigate through Kotter’s 8-Step Model and achieve long-term success.
Building a Guiding Coalition
One of the key elements in effectively implementing Kotter’s 8-Step Model is building a guiding coalition. This coalition consists of a diverse group of individuals who share a common goal and are committed to leading the change within the organization. The success of any change initiative heavily relies on the collaboration and leadership within this coalition.
So, how can you ensure that your guiding coalition is effective? Here are some techniques that can help:
- Communicate Clearly: Effective communication is crucial in building a guiding coalition. This includes sharing the vision, goals, and objectives of the change initiative, as well as addressing any concerns or questions that may arise. Clear and open communication helps to build trust and foster collaboration among coalition members.
- Choose the Right Members: It is important to carefully select members for your guiding coalition. Look for individuals who have the necessary skills, experience, and influence to drive change within the organization. Diversity in backgrounds, perspectives, and expertise can also bring valuable insights and ideas to the table.
- Establish a Shared Purpose: In order to work effectively together, the members of the guiding coalition must have a shared purpose and understanding of the change initiative. This can be achieved through team-building exercises, workshops, or other activities that foster collaboration and a sense of unity within the coalition.
By implementing these techniques, you can ensure that your guiding coalition is equipped with the necessary leadership and collaboration skills to successfully navigate organizational change using Kotter’s 8-Step Model.
Empowering Employees for Broad-Based Action
Kotter’s 8-Step Model emphasizes the importance of involving and motivating employees in the change process. This can be a challenging task, as employees may resist change or feel overwhelmed by it. However, by empowering employees and giving them a sense of ownership in the change, organizations can create broad-based action and ensure the success of their change initiatives.
One way to involve and motivate employees is to communicate openly and transparently about the change. This means sharing the reasons behind the change, the expected outcomes, and how it will impact employees. By keeping employees informed, they will feel more engaged and invested in the process.
Another strategy is to involve employees in decision-making processes. This not only gives them a sense of control but also allows them to contribute their unique perspectives and ideas. By involving employees, organizations can tap into their knowledge and expertise, making them more likely to support and actively participate in the change.
Organizations can also empower employees by providing opportunities for training and development. Change often requires new skills and competencies, and by investing in employee development, organizations can ensure that their workforce is equipped to handle the change effectively.
Finally, recognizing and rewarding employees for their contributions to the change is crucial. This can be done through incentives, promotions, or simply acknowledging their efforts and hard work. By recognizing and valuing employees’ contributions, organizations can foster a culture of continuous improvement and create a sense of pride and ownership in the change process.
Anchoring New Approaches in the Company’s Culture
One of the key challenges when implementing Kotter’s 8-Step Model for change management is anchoring new approaches in the company’s culture. This step is crucial for ensuring lasting and sustainable change within an organization.
To embed change into the organizational culture, leaders must first identify the core values and beliefs that drive the current culture. This will provide a foundation for understanding how to align the new approaches with the existing culture.
Next, it is important to communicate clearly and consistently about the changes and how they align with the company’s values and goals. This will help employees understand the purpose and importance of the changes, and encourage their buy-in and support.
Leaders should also lead by example and demonstrate the desired behaviors and attitudes that are expected from employees. This will help to create a culture of accountability and reinforce the importance of the changes.
Additionally, providing training and resources for employees to adapt to the new approaches will help to embed them into the organizational culture. This can include workshops, coaching, and other learning opportunities.
Finally, it is important to continuously monitor and assess the progress of embedding change into the culture. Leaders should gather feedback from employees and make adjustments as needed to ensure that the new approaches are truly embedded into the company’s culture.
Anchoring New Approaches in the Company’s Culture
One of the key aspects of successfully implementing Kotter’s 8-Step Model for change management is anchoring new approaches in the company’s culture. This means ensuring that the changes being made are not just temporary, but become a permanent part of how the organization operates.
To embed change into the organizational culture, there are a few important steps to follow:
- Communicate the Vision and Purpose: It is important to clearly communicate the reasons behind the change and how it aligns with the organization’s overall vision and purpose. This will help employees understand the importance of the change and feel more invested in it.
- Lead by Example: Leaders and managers must be role models for the desired changes. They should actively demonstrate the new behaviors and practices to show their commitment to the change.
- Incorporate Change into Processes and Systems: Change should not just be a one-time event, but rather integrated into the organization’s processes and systems. This will make it easier for employees to adopt new approaches and make them a habit.
- Celebrate Successes: When positive changes occur, it is important to celebrate and recognize them. This will help reinforce the new behaviors and motivate employees to continue embracing the changes.
By following these steps, organizations can successfully anchor new approaches in their culture, making change a natural part of how they operate. This will help ensure that the changes implemented through Kotter’s 8-Step Model have a lasting impact on the organization.
In conclusion, Kotter’s 8-Step Model provides a comprehensive framework for effectively managing change in organizations. By understanding and addressing the common challenges that may arise, leaders can successfully navigate change and achieve their desired outcomes. However, it is important to note that every organization is unique, and there is no one-size-fits-all approach to change management. It is crucial for leaders to continuously evaluate and adapt their strategies to best fit their specific context.